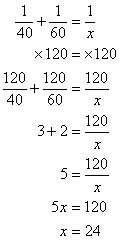Ang Work Problem ay isang word problem kung saan dalawa o higit pang tao ang nasasangkot na gumagawa ng isang trabaho na may IBA'T IBANG bilis (rate or speed) sa paggawa.
Halimbawa, kayang tapusin ni Juan ang pagbubunot ng sahig sa loob lamang ng tatlumpung minuto. Dalawampung minuto naman kapag si Pedro ang gumawa. Kung sabay nilang bubunutin ang sahig, ilang minuto nila itong tatapusin?
PARAAN:
1) Isulat natin ang ating mga Given at Variables:
Juan = 30 min. ===> ang oras (time) bahagi ng trabahong kanyang gagawin = 1/30
Pedro = 20 min. ===> ang oras (time) bahagi ng trabahong kanyang gagawin = 1/20
Kabuuan trabaho = x ===> ang kabuuang oras ng trabahong gagawin nina Juan at Pedro = 1/x
TANDAAN:
Mapapansin natin na ang RECIPROCAL ng numero ang bahagi ng trabahong gagawin.
Ano ba ang reciprocal? Ito ay ang kabaliktaran ng isang bilang.
Halimbawa, ang reciprocal ng 2 ay 1/2. Kaya ang reciprocal ng 1/2 ay 2.
Ang reciprocal ng 2/3 ay 3/2.
Ang reciprocal ng x ay 1/x.
Kuha na?
2) Isulat ang EQUATION
1/30 + 1/20 = 1/x
3) SAGUTIN
Hanapin ang LCD o Less Common Denominator==> ang pinakamaliit na numerong maaaring hatiin sa dalawang denominator na 30 at 20. Kung nahihirapan kayong hanapin ang LCD, maaaring i-multiply ninyo ang dalawang denominators na 30 at 20 at ito ang kuhanin. Maaari ring hanapin ang LCM o Less Common Multiple ==> ang pinakamaliit na product ng 2 denominators kung i-mumultiply sila sa counting numbers ( 1, 2, 3, 4 ... and so on)
Kung gayon ===> 30 x 20 = 600
Pagkatapos, i-multiply ang nakuhang product sa itaas sa BUONG EQUATION.
600 x (1/30 + 1/20 = 1/x)
20 + 30 = 600/x
50 = 600/x
x = 600/50
x = 12 min
Sa pagkuha ng LCD, maaaring isama na rin ang denominator ng ikatlong term o yong nasa kaliwa ( 1/x).
Kaya ang makukuhang product ay 600x
Kung magkagayun,
600x(1/30 + 1/20 = 1/x)
20x + 30x = 600
50x = 600
x = 600/50
x = 12 min.
SUMMARY
Sa kabuuan, ang formula sa pagsagot ng work problem kung saan iba't iba ang bilis ng paggawa ay:
1/t1 + 1/t2 = 1/tb
kung saan, t1 = time o oras ng unang tao
t2 = time o oras ng ikalawang tao
tb = kabuuang oras (time) ng dalawa
Ang pormulang nabanggit sa itaas ay maaaring gamitin sa dalawa o higit pang tao at sa mga pipes filling up a tank problem.
Halimbawa (from http://www.onlinemathlearning.com/math-work-problems.html)
Peter can mow the lawn in 40 minutes and John can mow the lawn in 60 minutes. How long will it take for them to mow the lawn together?
Solution:
Step 1: Assign variables:
Let x = time to mow lawn together
Step 2: Use the formula:
Step 3: Solve the equation
Multiply both sides with 120The LCM of 40 and 60 is 120
Answer: The time taken for both of them to mow the lawn together is 24 minutes.
Work Problem with one unknown time
Paano naman kung ang isa sa dalawa (o higit pang tao) ay hindi alam ang oras ng paggawa?
Halimbawa:
Jack can paint a house in 6 hours. If his brother, Dave helps, it takes them four and two-thirds hours. How long will it take Dave working alone?
1) Isulat ang Given at Variable
Jack = 6 hours : Time = 1/6 (Reciprocal)
Dave = x : Time = 1/x (Reciprocal)
Total Time = 4 2/3 = 14/3 : Time = 3/14 (Reciprocal)
2) Isulat ang Equation or Formula
1/6 + 1/x = 3/14
3) Sagutin ang Equation
Kung ayaw hanapin ang LCD, i-multiply na lang ang lahat ng denominators ( 6, x at 14)
6 times x times 14 = 84x
I-multiply ang nakuhang produkto sa itaas (84x) sa Equation
Kaya,
84x ( 1/6 + 1/x = 3/14)
84x/6 + 84x/x = 84x (3/14)
14x + 84 = 18x
18x = 14x + 84
4x = 84
x = 21 hours
Checking:
1/6 + 1/x = 3/14
since x = 21
1/6 + 1/21 = 3/14
6x21x14 = 1764
1764(1/6 + 1/21 = 3/14)
1764/6 + 1764/21 = 1764 (3/14)
294 + 84 = 5292/14
378 = 378
===============