Lesson 5 - Triangles
Bago natin suungin ang aralin tungkol sa triangle o trianggulo na siyang pinakabasehan ng Trigonometry, alalahanin nating muli ang ating mga napag-aralan na:
• An angle is formed by two rays with a common endpoint. The two rays are called the sides of the angle and the common endpoint is called the vertex.
• Angles are usually named using three capital letters of the English alphabet. But they can also be named using numbers or letters of the Greek alphabet.
• A protractor is an instrument used to measure an angle. The units of measurement for angles are degrees (°) or radians (r).
• Angles are classified according to their measurements.
• Acute angle — an angle whose measurement is less than 90°.
• Right angle — an angle whose measurement is exactly 90°.
• Obtuse angle — an angle whose measurement is more than 90°
but less than 180°.
• Straight angle — an angle whose measurement is exactly 180°.
• Reflex angle — an angle whose measurement is more than 180°
but less than 360°.
• If the sum of the measurements of two angles is 90°, they are complementary angles.
• To find the measurement of the complement of a given angle, subtract the measurement of the given angle from 90°.
• If the sum of the measurements of two angles is 180°, they are supplementary angles.
• To find the measurement of the supplement of a given angle, subtract the measurement of the given angle from 180°.
After learning all about angles in the previous lesson, you are now ready to tackle more complicated figures such as triangles. This lesson will focus on the different kinds of triangles. The knowledge you will gain from this lesson will hopefully help you in solving real-life problems.
Matapos mong malaman ang lahat tungkol sa mga anggulo sa nakaraang aralin, handa ka na ngayon upang harapin ang mas kumplikadong mga pigura tulad ng mga triangles. Ang aralin na ito ay magtutuon sa iba't ibang mga uri ng mga triangles. Ang kaalamang makukuha mo mula sa araling ito ay sana makatulong sa iyo sa paglutas ng mga problema sa totoong buhay.
Ano ang triangle?
A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles.
Ang trianggulo ay isang polygon na may tatlong gilid at tatlong anggulo.
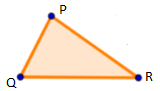
Masdan ang triangle sa itaas. Ang simbolo para sa isang trianggulo ay D. Tatawagin nating D QRP ang pigura sa itaas. Ang sides o mga gilid ng D QRP ay QR (RQ), QP (PQ), at RP (PR). Ang tatlong angles naman ay ÐQ, ÐR, at ÐP.
What are the different kinds of triangles?
A. Triangles are classified according to the lengths of their sides.
Ang mga trianggulo ay kinaklase ayon sa haba ng mga sides/gilid nito.
1. A scalene triangle is a triangle with no congruent side. Congruent means having the same or equal measure.
In the above figure, PQ ≠ QR ≠ PR, so ΔPQR is a scalene triangle.
2. An isosceles triangle is a triangle with two congruent sides.
3. An
equilateral triangle is a triangle with
three congruent sides.
B. Triangles are also classified according to the kinds of angles that make them up.
1. A triangle with a right angle is called a right triangle. A right angle measures 90 degrees.
2. A triangle that is made up of three acute angles is called an acute triangle. An acute angle measures more than zero degrees but less than 90 degrees.
3. A triangle with
an obtuse angle is called an
obtuse triangle. An obtuse angle measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees.
In summary, triangles are classified according to the lengths of their sides and the angles that they make up. See the illustration below from
https://www.cuemath.com to understand and remember the concept:
Pagsasanay
Upang matasa kung nauunawaan ang leksyon, sagutin ang mga sumusunod na katanungan:
1. Magkakasukat ang tatlong gilid o sides ng isang trianggulo. Ang triangle na ito ay tinatawag na __________ triangle.
A. right
B. equilateral
C. isosceles
D. acute
2. Isa sa mga angles ng triangle na ito ay may sukat na 91 degrees. Ang triangle na ito ay isang ________ triangle.
A. right
B. acute
C. obtuse
D. isosceles
3. Ang isosceles triangle ay may magkakaparehong sukat ng _______ gilid o sides.
A. isa
B. dalawa
C. tatlo
D. apat
4. May tatlong acute angles ang triangle na ito na hindi magkakapareho ang sukat. ________ triangle ang tawag dito.
A. acute
B. scalene
C. obtuse
D. right
5. Ang mga sides o gilid ng triangle na ito ay iba-iba ang mga sukat. Ang tawag sa triangle na ito ay ________ triangle.
A. equilateral
B. isosceles
C. reflex
D. scalene
6. Ang sukat ng mga angles ng isang equilateral triangle ay _________.
A. iba-iba
B. 30 degrees
C. 45 degrees
D. 60 degrees
7. Ang supplementary angle ng ÐY = 30 degrees ay _______ degrees.
A. 60
B. 90
C. 150
D. 330
8. Alin sa mga sumusunod na pares ang complementary angles?
A. Ð2 = 30o | ÐA = 30o
B. Ð3 = 35o | ÐB = 35o
C. Ð4 = 45o | ÐC = 45o
D. Ð5 = 90o | ÐM = 90o
9. Ang triangle na ito ay may dalawang gilid na magkakapareho ang sukat. _______ triangle ang tawag dito.
A. isosceles
B. equilateral
C. complementary
D. right
10. Ilang right angle mayroon ang isang right triangle?
A. wala
B. isa
C. dalawa
D. tatlo
Mga sagot sa pagsasanay