LESSON 7 – The Six Trigonometric Functions
Pagtutuunan natin sa araling ito ang tungkol sa anim (6) na Trigonometric Functions. Bago natin tukuyin ang mga katangian ng mga ito, balik-aralan muna natin ang mga bahagi ng right triangle kung saan nakabase ang anim na functions ng Trigonometry.
Sinasabing right triangle ang isang trianggulo o tatsulok kung ito ay may isang right angle. Ang right angle ay may sukat na 90 degrees (90o) o π/2 radian o 1.5708 radians ( 90 x π/180; where π≈ 3.1416).
Pagmasdan ang right triangle sa itaas:
Mayroong espesyal na pangalan para sa bawat gilid o side ng isang right triangle. Ang dalawang gilid ng ΔXYZ (triangle XYZ) na bumubuo ng right angle, XZ at YZ, ay tinatawag na mga binti o legs ng tatsulok. Ang pangatlong gilid, XY, ay tinawag na hypotenuse. Ang hypotenuse ay ang gilid sa tapat ng right angle. Ito ang pinakamahabang gilid/side ng right triangle.
Sukatin natin ang haba ng mga gilid ng right triangle:
XY = 25 units YZ = 7 units XZ = 24 units
Ang tatsulok sa itaas ay may 2 acute angles. Alalahanin na acute angle ang tawag sa anggulo o salikop na may sukat na mas malaki sa zero degree ngunit mas mababa sa 90 degrees.
Ang mga acute angles na ito ay ang∠X (angle X) at ∠Y (angle Y). Ang bawat isa sa mga ito ay naporma sa pamamagitan ng hypotenuse at isang leg o gilid. Ang ∠X ay produkto ng side XY at side XZ, samantalang ang ∠Y ay gawa ng side XY at side YZ.
Ang leg na kasama ng hypotenuse upang makagawa ng acute angle ay tinatawag na adjacent side/leg.
Sa ating halimbawang drawing sa itaas, ang leg/side adjacent sa ∠X ay side XZ (o XZ lamang). Ang leg naman adjacent sa ∠Y ay YZ. Dalawa ang side adjacent sa ∠Z; ito ay XZ at YZ.
Opposite side naman ang tawag sa gilid/side/leg na katapat ng angle na pinagbabatayan. Narito ang opposite side ng ating tatlong angle:
∠X ==> YZ ∠Y ==> XZ ∠Z ==>XY
Dapat tandaan na ang opposite side ng right angle (90 degrees) o ∠Z ay ang hypotenuse. Depende sa anggulo o salikop na pinagbabatayan, ang opposite side ng isang acute angle ay maaaring adjacent side naman ng isa pang acute angle at kabaliktaran o vice versa.
Halimbawa, ang opposite side ng ∠X ay YZ, samantalang ang YZ ay siyang adjacent side ng ∠Y; ang XZ ay ang opposite side ng ∠Y, samantalang ang XZ ay siyang adjacent side ng ∠X .
PAGSASANAY A
Batay sa drawing sa ibaba, sagutin ang mga tanong:
hypotenuse =
side adjacent to ∠A =
side opposite ∠A =
side adjacent to ∠B =
side opposite ∠B =
side opposite ∠C =
side/s adjacent to ∠C =
2. Batay sa drawing sa ibaba, sagutin ang haba ng mga gilid/side:
hypotenuse =
side/s adjacent to ∠A =
side opposite ∠A =
side adjacent to ∠B =
side opposite ∠B =
side opposite ∠C =
side adjacent to ∠C =
(Tunghayan ang mga sagot sa ibaba)
Matapos nating malaman ang mga parte o bahagi ng isang right triangle, handa na tayong kilalanin ang anim na trigonometric functions. Ang mga ito ay ginagamit upang hanapin ang nawawalang mga parte ng mga right triangles.
The Six Trigonometric Functions
1. Sine of an Angle
The sine of A is the ratio of the length of the side opposite A to the length of the hypotenuse. The sine of A is abbreviated as sin A.
Ang sine ng A (angle A) ay ang ratio ng haba ng gilid sa tapat ng A sa haba ng hypotenuse. Ang sine ng A ay dinaglat bilang sin A. Samakatuwid,
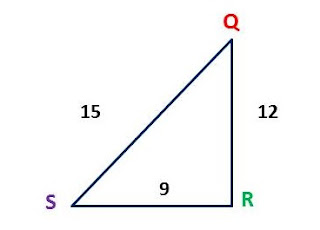
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
sin Q = opposite/hypotenuse = RS/QS = 9/15
sin S = opposite/hypotenuse = QR/QS = 12/15
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
sin D = opposite/hypotenuse = EF/DF = 24/26
sin F = opposite/hypotenuse = DE/DF = 10/26
2. Cosine of an Angle
The cosine of A (angle A) is the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to A and the length of the hypotenuse. The cosine of A is abbreviated as cos A.
Ang cosine ng A (angle A) ay ang ratio ng haba ng gilid katabi ng A sa haba ng hypotenuse. Ang cosine ng A ay dinaglat bilang cos A. Samakatuwid,
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
cos Q = adjacent/hypotenuse = QR/QS = 12/15
cos S = adjacent/hypotenuse = SR/QS = 9/15
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:

Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
cos D = adjacent/hypotenuse = DE/DF = 10/26
cos F = adjacent/hypotenuse = EF/DF = 24/26
3. Tangent of an Angle
The tangent of A (angle A) is the ratio of the length of the side opposite A and the length of the side adjacent to A. The tangent of A is abbreviated as tan A.
Ang tangent ng A (angle A) ay ang ratio ng haba ng gilid katapat ng A sa haba ng gilid kalapit ng A. Ang tangent ng A ay dinaglat bilang tan A. Samakatuwid,
tan A = length of side opposite A
length of side adjacent to A
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
tan Q = opposite/adjacent = SR/QR = 9/12
tan S = opposite/adjacent = QR/SR = 12/9
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
tan D = opposite/adjacent = EF/DE = 24/10
tan F = opposite/adjacent = DE/EF = 10/24
4. Cotangent of an Angle
The cotangent of A (angle A) is the reciprocal of the tangent of A. It is the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to A and the length of the side opposite A. The cotangent of A is abbreviated as cot A.
Ang cotangent ng A (angle A) ay ang kabaliktaran ng tangent ng A. Ito ay ang ratio ng haba ng gilid kalapit ng A sa haba ng gilid katapat ng A. Ang cotangent ng A ay dinaglat bilang cot A. Samakatuwid,
cot A = length of side adjacent to A
length of side opposite A
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
cot Q = adjacent/opposite = QR/SR = 12/9
cot S = adjacent/opposite = SR/QR = 9/12
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
cot D = adjacent/opposite = DE/EF = 10/24
cot F = adjacent/opposite = EF/DE = 24/10
5. Secant of an Angle
The secant of A (angle A) is the reciprocal of the cosine of A. It is the ratio of the length of the hypotenuse and the length of the side adjacent to A. The secant of A is abbreviated as sec A.
Ang secant ng A (angle A) ay ang kabaliktaran ng cosine ng A. Ito ay ang ratio ng haba ng hypotenuse sa haba ng gilid kalapit ng A. Ang secant ng A ay dinaglat bilang sec A. Samakatuwid,
sec A = hypotenuse
length of side adjacent to A
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
sec Q = hypotenuse/adjacent = QS/QR = 15/12
sec S = hypotenuse/adjacent = QS/SR = 15/9
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
sec D = hypotenuse/adjacent = DF/DE = 26/10
sec F = hypotenuse/adjacent = DF/EF = 26/24
6. Cosecant of an Angle
The cosecant of A (angle A) is the reciprocal of the sine of A. It is the ratio of the length of the hypotenuse and the length of the side opposite A. The cosecant of A is abbreviated as csc A.
Ang cosecant ng A (angle A) ay ang kabaliktaran ng sine ng A. Ito ay ang ratio ng haba ng hypotenuse sa haba ng gilid katapat ng A. Ang cosecant ng A ay dinaglat bilang csc A. Samakatuwid,
csc A = hypotenuse
length of side opposite A
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:
Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
csc Q = hypotenuse/opposite = QS/SR = 15/9
csc S = hypotenuse/opposite = QS/QR = 15/12
Pagmasdan ang pigura sa ibaba:

Ayon sa drawing sa itaas, makikita na:
csc D = hypotenuse/opposite = DF/EF = 26/24
csc F = hypotenuse/opposite = DF/DE = 26/10
PAGSASANAY B
1. Pagmasdan ang drawing sa ibaba at sagutin ang mga tanong:
sin A = sin C =
cos C = cos A =
tan A = tan C =
2.Pagmasdan ang drawing sa ibaba at sagutin ang mga tanong:
sin Y = sec Z =
cos Y = cot Z =
tan Y = csc Z
3. If sin B = 8/3, then csc B = ______.
A. 8/3 B. 3/8 C. 3/3 D. 8/8
4. If tan W = 12/13, then 13/12 is ______.
A. csc W B. sec W C. cos W D. cot W
5. Right Δ123 has sides 3, 4, and 5 units. The hypotenuse of the triangle is ______ units.
A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 12
6. Right ΔJKL has sides 9, 12, and 15 cm. If ∠K is the right angle and side JK = 12 cm, then cot L = _____?
A. 9/12 B. 12/15 C. 9/15 D. 12/9
Tandaan
• The two sides of the triangle that form the right angle are called its legs. The third side is called its hypotenuse.
• The leg that helps form an acute angle in a right triangle is said to be adjacent to that angle.
• The same leg is said to be opposite the other acute angle.
• The hypotenuse is always the side opposite the right angle and it is the longest side.
Upang matandaan ang formula para sa sine, cosine, at tangent, alalahanin ito:
SohCahToa, kung saan ang S = sine, o = opposite, h = hypotenuse, C = cosine, at T = tangent. Kaya,
Soh ==>sine A = o/h or opposite/hypotenuse
Cah==>cosine A = a/h or adjacent/hypotenuse
Toa==>tan A = o/a or opposite/adjacent
Tandaan din na:
Ang cotangent ay kabaliktaran ng tangent . Kung ang tan A = opposite/adjacent, ang cot A = adjacent/opposite.
Ang secant ay kabaliktaran ng cosine. Kung ang cos A = adjacent/hypotenuse, ang sec A = hypotenuse/adjacent.
Ang cosecant ay kabaliktaran ng sine. Kung ang sin A = opposite/hypotenuse, ang csc A = hypotenuse/opposite.
SAGOT SA PAGSASANAY